The impact of AI on the labor market is becoming increasingly evident as researchers delve into the ways artificial intelligence is reshaping the workforce. A recent study reveals that tech disruption jobs are evolving rapidly, highlighting the importance of understanding labor market trends in 2025. As automation in the workplace accelerates, many experts express concerns over job polarization AI, wherein high-skill roles proliferate while low-wage positions decline. This shift prompts discussions about the future of the artificial intelligence workforce and its implications for job security across industries. The ongoing transformation underscores the necessity for individuals to adapt and reskill to thrive in an AI-driven economy.
The influence of artificial intelligence on employment patterns has emerged as a critical discussion point in the modern economy. As technology advances, the characteristics of the workforce are altering, leading to significant changes in job availability and skills demand. This tech revolution raises important questions regarding how individuals will navigate their careers amid growing automation and evolving labor market dynamics. The evolving landscape calls for a closer examination of workforce readiness and adaptation strategies for the future. Understanding these shifts is vital for workers seeking to maintain relevance in an increasingly automated job environment.
The Evolving Landscape of the Labor Market
The U.S. labor market has undergone a significant transformation over the past century, driven by technological advancements. The study co-authored by economists Deming and Summers sheds light on this evolving landscape, illustrating how changes in technology, particularly artificial intelligence, have reshaped the distribution of jobs across various sectors. As researchers analyze over 100 years of data, they highlight key moments of disruption, particularly from the 1990s onwards, when technology began exerting its influence more intensely, leading to shifts in occupational categories.
In examining labor market trends toward 2025, it becomes evident that occupations traditionally dominated by middle-skilled jobs face dire straits. While highly skilled positions have surged, low-wage roles continue to experience stagnation or decline. This divergence in job growth trends points to a new era where continuing education and technological adaptiveness will play pivotal roles in shaping the workforce. As industries adapt to the changing environment, workers must equip themselves with skills that align with the emergent demands in sectors like STEM and technology-driven services.
AI’s Impact on Labor Market Trends
The impact of artificial intelligence on the labor market cannot be overstated. As noted in the research, AI is not merely a futuristic concept but a present reality that is actively reshaping the workforce. From automation in the workplace to enhanced decision-making capabilities, AI technologies are being leveraged to improve productivity across various sectors. This shift is indicative of a broader tech disruption that results in both the creation of new high-wage jobs while simultaneously threatening low-wage positions, highlighting a trend toward job polarization.
Labor market trends suggest that as AI continues to be integrated into business practices, the demand for skilled workers who can harness this technology will rise. This is evidenced by the significant growth within STEM jobs, which have increased as businesses prioritize technological capabilities. However, as AI takes on roles traditionally filled by humans, coupled with a minimized need for low-skill labor, it raises critical questions about future employment landscapes and job security for millions of workers.
Job Polarization and Its Consequences
Job polarization emerges as a significant theme in the ongoing dialogue about the future of work. Defined by the growth of both high-wage and low-wage jobs with simultaneous erosion of middle-skill roles, job polarization highlights the bifurcation of opportunities in the labor market. Research indicates that this pattern is exacerbated by advancements in artificial intelligence, which tend to augment roles that require advanced skills while automating routine tasks, predominantly affecting lower-skill jobs.
The consequences of this trend are profound, suggesting a pressing need for re-skilling initiatives that cater to the evolving demands of the labor market. As occupations continue to diversify and change, workers must not only navigate their current roles but also prepare for future shifts dictated by AI advancements and automation. Policymakers and educational institutions are increasingly tasked with addressing these needs to ensure a balanced labor market that mitigates the adverse effects of job polarization.
Automation and Its Role in Workforce Displacement
The rise of automation has led to considerable anxiety around job displacement, a concern that has only amplified with the advent of AI technologies. Various studies, including the one by Deming and Summers, reveal that significant portions of the traditional labor market face unprecedented volatility due to repetitive tasks being successfully executed by machines. This raises concerns not just about displacement but the urgency for the workforce to adapt proactively to the realities of automation.
Moreover, the integration of AI is not solely about job loss; it also engenders opportunities for new roles that focus on oversight, maintenance, and strategic execution within automated systems. While some positions in sectors like retail and low-wage services may vanish, others will emerge, emphasizing the critical intersection between skilled labor and technology. Companies are increasingly relying on skilled workers to adapt and enhance AI capabilities—positioning human capital as a vital asset in navigating the transition to a more automated economy.
Future-Proofing the Workforce through Education
With the labor market continuously evolving under the weight of technological disruption, future-proofing the workforce through education becomes paramount. The rise of AI and automation necessitates a reevaluation of educational curricula to foster the development of skills aligned with contemporary job demands. As highlighted in the Harvard paper, a focus on STEM education is crucial to minimizing the skills gap and preparing the next generation for careers that will dominate the future labor market.
Educational institutions are encouraged to adopt a forward-thinking approach that incorporates not only technical skills but also critical thinking, creativity, and adaptability into their programs. By doing so, they can equip students and workers with the essential tools to navigate a labor market characterized by constant change. This is particularly important for combating the implications of job polarization and ensuring that workers are not left behind as AI technologies become more prevalent.
Economic Insights into AI-Driven Job Transformation
From the perspective of economic implication, the integration of AI into the workforce offers both promise and challenge. The Harvard study underscores how AI has already begun to reshape job distribution across various sectors, leading to a dramatic increase in STEM job opportunities while traditional roles decline. Understanding these economic insights helps us to see the broader implications of technological advancements on wages, employment opportunities, and overall economic health.
Furthermore, businesses are increasingly investing in AI technologies, leading to a demand for workers who can effectively leverage these tools. This investment signals not only a shift in productivity measures but also an acknowledgment of the changing skill sets that will be required in the future. Professionals in industries like finance, management, and journalism must adapt to these insights to ensure their continued relevance in increasingly automated environments.
Tech Disruption: Lessons from the Past
Examining historical patterns of technological disruption can provide valuable insights into the current labor market dynamics. As illustrated in the study, previous waves of innovation—from the advent of electricity to the rise of the internet—have been accompanied by both displacement and the creation of new job categories. The key lesson is that while technology often displaces jobs, it also engenders new opportunities that can lead to enhanced productivity and economic growth.
However, not all segments of the workforce benefit equally from these transitions. The lessons from the past stress the importance of developing policies and strategies to support workers impacted by automation and AI. As history shows, proactive engagement with the challenges posed by new technologies can yield a more resilient economic landscape, allowing both businesses and workers to adapt successfully to the changing tides of the labor market.
Adjusting to a New Economic Reality
As we navigate the implications of AI and automation, adjusting to the new economic reality becomes essential. This involves acknowledging that while technology may create efficiencies, it also necessitates a workforce that can engage with these advancements meaningfully. The narrative around job displacement must shift to encompass the potential for job creation through innovation and the need for adaptive skill sets in a rapidly changing market landscape.
With the economic landscape ever-evolving, businesses must commit to fostering an adaptable workforce through investments in training and development. Employees need to be prepared not just to fulfill their current roles but to transition into new positions required by advancing technology. Embracing lifelong learning and adaptability will be critical in ensuring that workers are equipped to thrive amidst the backdrop of ongoing technological change.
The Role of Policy in Shaping Future Workforces
As we confront the challenges brought about by AI and technological advancement, the role of policy becomes increasingly prominent in shaping future workforces. Effective policies that promote education, skill development, and retraining programs will be crucial in mitigating the effects of job displacement. The insights from the recent study stress the need for a collaborative approach involving governments, educational institutions, and private sectors to lay the groundwork for a workforce equipped to meet future demands.
Additionally, policymakers must consider enacting measures that provide safety nets for workers who may find themselves displaced due to the rapid pace of technological change. By promoting inclusivity in the labor market and emphasizing equitable access to new technology and training, we can work towards an economic environment that celebrates innovation while ensuring that all workers are empowered to succeed amidst the shifts brought about by AI.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is AI impacting the labor market currently?
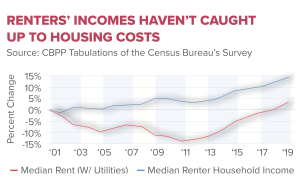
AI is significantly shaking up the labor market by changing job distributions, leading to an increased demand for high-skilled workers while decreasing opportunities for low-wage service jobs. Research indicates a notable shift in labor market trends since 2019, suggesting that AI plays a critical role in shaping employment patterns.
What are the trends in labor market volatility driven by AI?
The recent research by economists highlights four key trends influenced by AI: a decline in job polarization, a surge in high-skilled STEM positions, a drop in low-wage service jobs, and a significant reduction in retail sales jobs due to tech advancements. These trends suggest that AI is reshaping the workforce landscape.
What does job polarization mean in the context of AI’s impact on the labor market?
Job polarization refers to the widening gap in job growth between low-wage and high-wage positions. AI is reportedly ending this trend by favoring high-paid jobs that require advanced skills, indicating a shift towards a more skilled workforce as technology continues to evolve.
Will automation in the workplace lead to massive job losses?
While automation in the workplace, driven by AI, may lead to job displacement in some sectors, it also creates new opportunities in tech-related fields. The current data suggests that the job market is evolving rather than experiencing catastrophic job losses, with a focus on higher-skilled roles.
What sectors are most affected by AI’s influence on labor market trends?
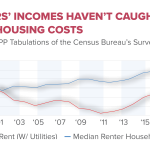
AI’s influence is most strongly felt in sectors like retail, where predictive technologies have reduced the share of sales jobs significantly. Additionally, low-wage service markets are experiencing decline, while sectors such as STEM are seeing substantial growth due to increasing investments in technology.
How can workers prepare for the changes in the labor market due to AI?
Workers can prepare for the labor market changes driven by AI by enhancing their skills, particularly in technology and STEM fields. As AI continues to evolve, familiarity with advanced technologies and adaptability will be crucial for job security and growth.
What role does AI play in shaping job distribution within the economy?
AI is reshaping job distribution by fostering demand for highly skilled labor while displacing lower-skill jobs. This evolution demonstrates a clear trend towards requiring greater technical knowledge, pushing the workforce to adapt to new technologies and workflows.
Are there risks associated with AI’s impact on labor market trends?
Yes, while AI offers productivity boosts, it poses risks of displacement for workers who lack proficiency with new technologies. This could lead to increased pressure on knowledge workers as companies expect rapid performance improvements due to AI capabilities.
| Trend | Description | Impact on Labor Market |
|---|---|---|
| End of Job Polarization | Shift towards well-paid jobs for highly skilled workers. | Decline in availability of middle-wage jobs; increased focus on skilled positions. |
| Surge in STEM Jobs | Significant increase in jobs related to science, technology, engineering, and math. | UM set to create more opportunities in tech-related fields. |
| Decline in Low-Wage Service Jobs | Jobs in low-wage sectors have faced stagnant or declining trends since 2019. | Reduced job security in lower-paying service industries. |
| Decrease in Retail Sales Jobs | Drop in retail sales jobs due to technological advancements and pandemic-induced habits. | Reconfiguration of retail jobs with a shift towards e-commerce and AI integration. |
Summary
The AI impact on the labor market is becoming increasingly evident as evidence suggests that artificial intelligence is disrupting traditional job structures. Recent research indicates significant changes in employment trends, particularly in favor of higher-skilled positions while diminishing opportunities in low-wage jobs. Many sectors, such as retail and service industries, are witnessing shifts that may not rebound, signifying a profound transition in how work is structured. With the growing investment in AI technologies, professionals across all fields must adapt and consider how these changes will shape their careers moving forward.