The prospect of a recession in the U.S. economy looms larger as recent trade tensions and economic indicators paint a troubling picture. The ongoing trade war has created uncertainty that significantly impacts investor confidence, while the Federal Reserve faces critical decisions about interest rates amidst falling consumer sentiment. With the consumer sentiment index dipping to its lowest since late 2022, fears are mounting that these factors could spiral into a recession. Furthermore, the effects of tariffs imposed in response to President Trump’s policies have reverberated through various sectors, exacerbating the perception of risk among consumers and investors alike. As the Federal Reserve deliberates potential rate cuts, the delicate balance between stimulating growth and managing inflation becomes increasingly challenging, making the health of the U.S. economy a focal point for analysts and policymakers alike.
As discussions surrounding the downturn of the U.S. economy intensify, many are raising alarms about the increasing possibility of economic contraction. This downturn, often referred to in the financial sector as an economic slowdown, complicates the fiscal landscape further due to influential factors such as international trade disputes and fluctuating consumer confidence. The current sentiment in financial markets suggests a pervasive uncertainty that could stem from the recent imposition of tariffs, which many experts argue may lead to worse economic conditions. Moreover, recent reports indicate a significant drop in the consumer confidence index, pointing towards a troubling trend that could foreshadow broader economic challenges. Policymakers are now tasked with navigating these treacherous waters, as decisions about interest rates loom large on the horizon.
The Current U.S. Economy: Signs of a Recession Ahead
As we look toward the future, signs suggest that the U.S. economy may be on the brink of a recession. The recent decline in the consumer sentiment index to its lowest point since November 2022 underscores a significant deterioration in economic confidence. Economists point to a combination of factors fueling these concerns, including ongoing trade wars and uncertainty surrounding Federal Reserve interest rates. With tariffs affecting the costs of imports and domestic goods, many households are feeling the pinch, leading to diminished spending and investment.
Moreover, the potential for a prolonged recession is enhanced by the unpredictability of governmental policy, particularly in regard to tariffs. The trade war initiated by the current administration has created a ripple effect across various industries, causing investors to reassess their strategies in light of rising global tensions. If these trends continue unchecked, the U.S. economy could experience a downturn that mirrors past recessions, negatively impacting employment rates and overall economic growth.
Tariffs and Their Impact on the U.S. Economy
The current tariff policies implemented by the federal government have had a marked impact on trade relations and domestic markets. Initially introduced as a means to protect American industries, these tariffs have instead resulted in increased costs for consumers and businesses alike. The cascading effects of these tariffs have been felt across various sectors, leading to heightened inflation and economic uncertainty, contributing to the concern of a looming recession. Trade dynamics have shifted, and American companies are faced with higher prices for imported goods, which in turn affect consumer prices and confidence.
Economic analysts warn that the adverse effects of high tariffs can ripple through the economy, stifling growth and innovation. Elevated import costs can lead to reduced consumer spending as individuals prioritize essential goods over luxury items. Furthermore, the uncertainty surrounding trade policies often leads to hesitation in long-term investments by businesses, creating a feedback loop where economic growth stalls. If the tensions between the U.S. and its trading partners persist, the potential for a recession becomes increasingly likely due to these unresolved tariff issues.
The Federal Reserve’s Dilemma: Interest Rates and Economic Stability
The Federal Reserve currently faces a challenging dilemma as it contemplates its next moves regarding interest rates. On the one hand, there is pressure to cut rates to stimulate economic growth amidst fears of a recession. On the other hand, maintaining higher interest rates is crucial for ensuring inflation does not spiral out of control. This precarious balancing act is made more difficult by external factors such as the ongoing trade war and fluctuating consumer sentiment. Higher tariffs can lead to increased prices, which may push inflation beyond the Fed’s comfort zone.
Given the current economic climate, it is likely that the Federal Reserve will opt for a cautious approach, potentially keeping interest rates unchanged for the time being. This decision would reflect the need to foster economic stability while also being mindful of inflationary pressures. Additionally, any sudden changes in policy could further exacerbate market volatility and consumer uncertainty. As investors and businesses navigate this unpredictable landscape, their confidence in the economy will hinge significantly on the Fed’s ability to effectively manage interest rates amidst the challenges posed by tariffs and consumer sentiment.
Consumer Sentiment: A Key Indicator of Economic Health
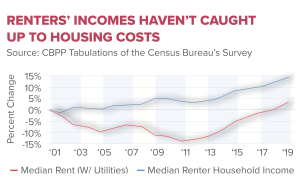
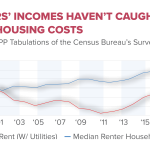
Consumer sentiment is a critical barometer of economic health, and its recent decline signals potential trouble ahead for the U.S. economy. As reported, the consumer sentiment index has plunged to its lowest level since late 2022, indicating a growing unease amongst American households. This decline in sentiment can be attributed to various stressors, including rising prices driven by tariffs, economic uncertainty, and a volatile stock market. When consumers feel less confident about their financial stability, they are less likely to spend, which can lead to slowed economic growth.
Furthermore, the implications of weakened consumer sentiment stretch beyond immediate spending patterns; they can also have long-term effects on business expansion and investment decisions. Companies may become reluctant to commit to new projects or hire additional staff when they perceive that consumers are hesitant to spend. This caution can contribute to a cycle of economic stagnation, often culminating in reduced GDP growth and potentially leading to a recession if the trend continues. As such, revitalizing consumer sentiment is essential for fostering a healthy economic landscape.
Impact of Stock Market Volatility on Economic Confidence
Recent stock market volatility has been a significant factor affecting economic confidence in the U.S. With investors reacting to geopolitical tensions and domestic policy changes, market fluctuations can trigger widespread uncertainty. Economists note that heavy sell-offs in the stock market often lead to diminished consumer and business confidence, creating a ripple effect that dampens economic activity. As the market descends, individuals may feel less secure about their investments and personal financial situations, leading to reduced spending.
Moreover, the correlation between stock market performance and consumer confidence is particularly pronounced. If the stock market is perceived as unstable, consumers may curtail spending in anticipation of economic downturns. This cautious approach can lead to decreased demand for goods and services, further affecting economic growth. The question remains whether the Federal Reserve’s responses to these market fluctuations will be enough to bolster confidence or if unpredictability will continue to influence investor and consumer behavior in the face of an uncertain economic future.
Evaluating the Long-Term Effects of the Trade War
As the trade war escalates with multiple nations imposing tariffs, a long-term analysis reveals substantial implications for the U.S. economy. While initially touted as a means to protect domestic industries, these tariffs have resulted in significant backlash, including retaliatory measures from trading partners. This escalating cycle of tariffs can lead to a decrease in international trade, harming U.S. exporters and compelling them to raise prices, which ultimately burdens consumers. Over time, these developments could lead to a contraction in economic growth and escalate existing pressures contributing to a potential recession.
In addition to immediate economic repercussions, the trade war also has broader geopolitical implications that can jeopardize U.S. influence in global markets. As relations sour, foreign investors may reconsider their positions in U.S. assets, leading to increased volatility in financial markets. The interplay between trade, tariffs, and shifting consumer sentiment creates a precarious environment that could yield prolonged economic instability if not addressed effectively. An analysis of these developments underscores the necessity of fostering constructive international relationships to stabilize and enhance economic sentiment moving forward.
Looking Ahead: Strategies for Economic Recovery
In light of the present challenges facing the U.S. economy, it’s crucial to explore potential strategies for a sustainable recovery. Policymakers must focus on restoring consumer confidence and stabilizing the market. Options such as reevaluating tariff policies, introducing targeted stimulus measures, and investing in critical infrastructure can help to mitigate the effects of current economic pressures. By prioritizing long-term economic health over short-term gains, stakeholders can work collaboratively towards enhancing overall economic sentiment.
Additionally, fostering open communication between the Federal Reserve and market participants is essential. Clear guidance regarding monetary policy and a strategic approach toward interest rates can help enhance stability and reduce uncertainties. By addressing the underlying causes of economic strain, including tariffs and trade wars, the U.S. can pave the way for recovery. Ultimately, engaging in cooperative measures may serve as a foundation for resilience and growth in the years to come, steering the U.S. economy away from potential recession.
The Role of Inflation in Economic Policy Decisions
Inflation plays a decisive role in shaping economic policy decisions as the Federal Reserve grapples with its dual mandate of promoting maximum employment and price stability. Current inflationary pressures, exacerbated by tariffs on goods, have forced policymakers to consider how rising prices may impact consumer behavior and overall economic growth. As inflation rates climb, the Fed must weigh the benefits of cutting interest rates against the potential risks of worsening inflation, creating a challenging environment for economic planning.
It is essential for the Fed to strike a balance if it aims to foster conditions conducive to economic recovery. When inflation is perceived as a threat, the Fed may be inclined to keep interest rates higher, which could stymie consumer spending and investment. Conversely, lowering rates in response to economic slowdowns could lead to further inflationary pressures if producers begin to pass on elevated costs to consumers. As policymakers navigate these turbulent waters, thoughtful consideration of inflation’s role in shaping sustainable growth will be paramount.
The Outlook for Employment: Navigating Economic Challenges
Employment remains a vital indicator of economic health, and current trends suggest that hiring is slowing amidst heightened uncertainty. The decision-making environment for businesses has grown increasingly complex, with many companies adopting a cautious stance in light of tariffs and market volatility. Job growth is often reflective of consumer confidence; when consumers hesitate to spend, businesses may scale back on hiring efforts, potentially leading to a stagnation in job creation and a downward spiral that contributes to recessionary pressures.
Policies aimed at stimulating job growth will be essential as the U.S. navigates the challenges of the current economy. Investing in workforce training and revitalizing key industries can help mitigate the negative impacts of slow hiring. Furthermore, creating an environment that fosters innovation and entrepreneurship will be pivotal in reversing current employment trends. By addressing labor market challenges head-on, policymakers can work toward ensuring a robust and resilient job market capable of supporting economic recovery in the face of uncertainty.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the impact of the U.S. economy recession on consumer sentiment index?
The U.S. economy recession has significantly affected the consumer sentiment index, which measures how optimistic or pessimistic Americans feel about the economy’s health. During recessionary periods, this index tends to decline, reflecting decreased economic confidence among consumers due to rising uncertainty, job losses, or increased prices.
How do Federal Reserve interest rates influence the U.S. economy recession?
Federal Reserve interest rates play a crucial role during a U.S. economy recession. By lowering interest rates, the Fed aims to stimulate economic activity by making borrowing cheaper, encouraging both consumer spending and business investment. Conversely, if rates are too high, it may stifle growth and contribute to prolonged recession.
What is the relationship between trade war impact and the U.S. economy recession?
The trade war impact is a significant factor in the U.S. economy recession, as increased tariffs can lead to higher costs for consumers and reduced profitability for businesses. This results in decreased consumer spending and investment, ultimately contributing to an economic slowdown.
Are tariffs effects a direct cause of the U.S. economy recession?
Yes, tariffs effects can be a direct cause of the U.S. economy recession. When tariffs are imposed, they can lead to higher prices for imported goods, disrupt supply chains, and reduce overall trade, negatively impacting economic growth and employment.
How does economic confidence relate to the U.S. economy recession?
Economic confidence is closely linked to the U.S. economy recession. A decrease in economic confidence often precedes a recession, as consumers and businesses become more cautious in their spending and investment decisions, fearing that economic conditions will worsen.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Cause of Concern | Heavy losses in U.S. markets due to tariffs imposed by China, Mexico, and Canada in response to U.S. tariffs. |
| Consumer Sentiment | The University of Michigan’s consumer sentiment index has declined to its lowest level since November 2022, indicating decreased confidence. |
| Trade War Risks | Concerns about a prolonged trade war worsening economic conditions, potentially leading to recession. |
| Market Response | Treasury Secretary calls the market selloff a normal correction, which contravenes economic reasoning according to experts. |
| Factors Leading to Recession | 1. Ongoing trade war 2. Stock market crash 3. Cuts in government spending 4. U.S. fiscal crisis 5. Increased risk perception due to unpredictability. |
| Federal Reserve Actions | The Fed faces a tradeoff in deciding whether to cut interest rates to support the economy or maintain rates to control inflation. |
Summary
The U.S. economy recession is a pressing concern as recent economic indicators suggest a potential downturn. Tariff-related tensions and a significant drop in consumer confidence are contributing factors that could push the economy into recession. With the Federal Reserve caught in a dilemma over interest rates and various other uncertainties at play, the risks have become considerably elevated. This precarious situation paints a troubling picture for the U.S. economy as it navigates through these turbulent times, highlighting the need for prudent policymaking and strategic economic responses to avert a full-blown recession.