The recent Federal Reserve rate cut has sparked discussions about its impact on the economy, particularly concerning mortgage rates and consumer spending. As the Fed lowers interest rates, individuals with existing debts and prospective homebuyers stand to benefit, with economists like Fed Chairman Jerome Powell suggesting that more rate cuts could be on the horizon. This strategic move, aimed at stimulating economic growth, promises to enhance housing affordability during a time when many are grappling with rising costs. Analysts are particularly optimistic about the trickle-down effects of these interest rate cuts on Wall Street and Main Street alike, with potential boosts in job creation and available credit. Thus, understanding the economic impacts of rate cuts and their broader implications is crucial for consumers and investors navigating this changing financial landscape.
The recent decision by the Federal Reserve to lower borrowing costs marks a significant shift in its monetary policy, one that many are closely watching. This interest rate adjustment, the first in four years, is anticipated to ease financial pressures for consumers and businesses alike. With heightened attention to housing dynamics and affordability, the implications of such a strategy extend beyond immediate savings on loans. Fed chair Jerome Powell has indicated a readiness for additional cuts down the line, aiming to foster a healthier economic environment. As markets absorb this news, the cascading effects on various sectors, particularly housing and consumer spending, emerge as pivotal areas of analysis.
Understanding the Federal Reserve Rate Cut and Its Purpose
The recent Federal Reserve rate cut marked a significant turning point for the U.S. economy, as it was the first reduction in interest rates in four years. This cut of half a percentage point, while larger than typical adjustments, aligns with the Fed’s ongoing strategy to stimulate economic growth amid fluctuating inflation rates. As noted by Fed Chairman Jerome Powell, this action was taken in response to encouraging signs in the economy, and it aims to enhance consumer spending by lowering borrowing costs. Understanding this context is crucial for assessing how such a policy can bolster economic activity across various sectors.
The purpose behind the Fed’s decision to implement this interest rate cut is multi-faceted; it addresses current economic conditions while also laying the groundwork for coping with future uncertainties. By easing monetary policy, the Fed strives to reduce the financial burden on consumers holding credit card debt and seeking mortgage loans, thus making it easier for them to manage their finances. As a result, lower rates could promote consumer confidence, encouraging spending, which is a driving force of economic growth.
Impacts on Mortgage Rates and Housing Affordability
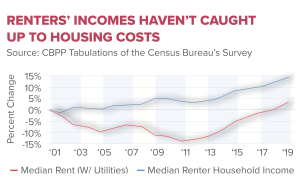
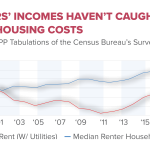
Following the Fed’s rate cut, mortgage rates are expected to trend downwards, offering potential relief for homebuyers navigating the current housing market. High mortgage rates have contributed significantly to housing affordability issues, making it increasingly challenging for potential homeowners to secure financing. As the Fed continues to ease its monetary policy, it is anticipated that these rates will continue to decrease, ultimately enhancing the ability for individuals to afford homes and invest in property.
However, while a decline in mortgage rates could alleviate some housing market pressures, the extent of this relief may vary. As economist Jason Furman noted, even with decreasing rates, the overall mortgage costs may still remain relatively high compared to previous years. This paradox highlights the critical balance the Federal Reserve must maintain in fostering economic growth while managing inflation levels so as not to exacerbate housing pricing issues. Hence, while consumers may benefit from lower rates, the overarching challenge of housing affordability persists due to other market dynamics.
The Economic Implications of Federal Reserve’s Rate Decision
The economic implications following the Federal Reserve’s decision to cut rates extend beyond just consumer borrowing; they resonate throughout the entire economy. Lower interest rates generally encourage businesses to invest more in growth, which in turn can lead to job creation and contribute positively to the labor market. This concurrent improvement in job growth, along with decreased consumer debt payments due to lower borrowing costs, can further stimulate spending habits, thereby propelling the economy forward.
Furthermore, the intention behind the Fed’s cut is to foster a more robust economic environment capable of withstanding potential future shocks. By enhancing liquidity in the market through these rate adjustments, the Fed provides a safeguard, allowing both consumers and businesses to navigate uncertainties more effectively. However, this balancing act also involves careful monitoring of inflation, which remains a significant concern. Too much easing could re-ignite inflationary pressures, complicating the Fed’s efforts to maintain economic stability.
Future Projections: What More Rate Cuts Could Mean
Looking ahead, there is speculation that the Federal Reserve may implement further rate cuts as economic conditions evolve. The indication of two additional cuts by the end of the year points to a proactive approach by the FOMC, especially given the economic signals they are monitoring closely, such as inflation and unemployment rates. This forward guidance from the Fed serves to reassure both consumers and investors that they are prepared to mitigate adverse economic conditions through strategic monetary policy adjustments.
However, it’s critical to acknowledge that these projections come with caveats. Future economic data will significantly influence the Fed’s decision-making process, and if inflation were to accelerate unexpectedly, the committee may decide to halt the proposed rate cuts. This uncertainty necessitates a careful approach from businesses and consumers alike, as the potential for further rate cuts could shift market expectations and spending behavior. Understanding this interplay will be vital in navigating the upcoming economic landscape.
Fed Chairman Jerome Powell’s Role in Economic Policy
As the face of the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy, Chairman Jerome Powell plays a pivotal role in shaping the economic narrative surrounding interest rates. His leadership style and decision-making process directly impact how the Fed approaches economic challenges, particularly in times of uncertainty. Powell’s recent comments indicate a commitment to adaptive monetary strategies, which aim to balance inflation management with economic growth initiatives. This is evident in his advocacy for timely rate adjustments that can stimulate consumer spending and investment.
Powell’s ability to communicate complex economic concepts in an accessible manner also aids in building public confidence in the Fed’s actions. By conveying the rationale behind rate decisions and the subsequent anticipated outcomes, Powell reinforces the Fed’s credibility among investors and consumers alike. His approach to leadership embodies the Fed’s focus on transparency, making it easier for stakeholders to anticipate how future economic shifts might influence their financial situations.
Consumer Reactions to Interest Rate Cuts
The announcement of the Federal Reserve’s interest rate cut has elicited a range of reactions among consumers, particularly those burdened by high-interest debts. For many, the prospect of lower rates on credit cards and loans translates to immediate financial relief, providing a much-needed breathing space. Consumers who had been hesitant to make major purchases due to high borrowing costs may now feel encouraged to invest in homes, cars, or durable goods as the cost of financing decreases.
However, there is also caution among consumers regarding how sustained lower rates might impact their long-term financial strategies. Some may worry about the future implications of an economy that relies heavily on low interest for growth. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for consumers, as they navigate their financial landscapes while making educated decisions about spending, saving, and investing in a fluctuating economic climate.
The Broader Economic Outlook Following Rate Cuts
The broader economic outlook post-rate cuts hinges on several factors including consumer behavior, business investment, and global economic conditions. While the immediate effects of lower interest rates are often positive, fostering increased liquidity and consumer spending, the long-term impacts can be more complex. A sustained period of low rates could lead to distortions in asset markets and potential challenges for the Fed in controlling inflation if the economy overheats.
Additionally, external factors such as geopolitical tensions and global supply chain issues can further complicate the economic outlook. As such, the Federal Reserve’s ability to navigate these challenges will play a crucial role in maintaining economic stability. Ongoing assessments and strategic adjustments to monetary policy will be essential as the Fed seeks to support economic growth while managing inflationary pressures and promoting overall financial health.
Market Expectations Following a Rate Cut
Market expectations often shift in response to significant actions taken by the Federal Reserve, particularly interest rate cuts. Following such announcements, financial markets can react quickly, reflecting changes in anticipated economic conditions. Investors typically adjust their portfolios in anticipation of lower borrowing costs, reallocating resources into sectors that are more sensitive to changes in interest rates, such as real estate and consumer goods.
Furthermore, the psychological impact of a rate cut cannot be understated; it often imbues the market with a sense of optimism regarding future economic growth. This change in sentiment encourages greater risk-taking among investors, which can result in increased stock market activity. The Fed’s mandates to promote maximum employment and stable prices serve as guiding principles for market participants, who closely monitor fiscal policies to make informed investment decisions.
Long-Term Effects of Interest Rate Adjustments on Consumers
The long-term effects of interest rate adjustments can have profound implications for consumers, shaping their spending habits and financial health over time. Lower rates may encourage consumers to take on more debt, believing that they can manage repayments better during favorable economic conditions. However, this reliance on low-interest financing poses risks if economic conditions shift unexpectedly, potentially leading to financial strain.
Additionally, while lower borrowing costs may initially boost consumer spending, a prolonged low-rate environment could foster complacency regarding debt management habits. It is imperative for consumers to remain vigilant about their financial strategies; understanding market conditions and preparing for potential rate increases in the future can help them maintain financial stability. As they navigate these changes, awareness and education about the economic landscape will be critical for informed decision-making.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current Federal Reserve rate cut decision and its significance?
The Federal Reserve recently cut a key interest rate by half a percentage point, marking its first rate cut in four years. This decision aims to reduce borrowing costs for consumers, especially benefiting those with credit card debt and prospective homebuyers. The move signals the Fed’s commitment to managing inflation while supporting economic growth.
How does the Federal Reserve rate cut affect mortgage rates?
The recent Federal Reserve rate cut is expected to lead to lower mortgage rates in the coming months, improving housing affordability. While mortgage rates have decreased recently, they remain relatively high, but continued easing of policy by the Fed is likely to further reduce these rates.
What potential additional Federal Reserve rate cuts might occur this year?
Economists anticipate that the Federal Reserve could implement two more rate cuts of 25 basis points each by the end of the year, depending on future economic data. Fed Chairman Jerome Powell indicated that the Fed is prepared to take further action if necessary, signaling strong support for more cuts.
How does the Federal Reserve’s rate cut impact consumers with credit card debt?
Consumers with credit card debt may benefit from the recent Federal Reserve rate cut as it lowers borrowing costs. As the Fed continues to ease its policy, consumers can expect a gradual decline in interest rates, potentially easing the burden of credit card repayments.
What are the broader economic impacts of the Federal Reserve rate cuts?
The Federal Reserve rate cuts are projected to stimulate modest economic growth and job creation in the short term. While immediate impacts may be limited, over the next six to twelve months, the easing of monetary policy could lead to positive effects on employment and inflation.
How should consumers prepare for the effects of the Federal Reserve’s rate cut on their finances?
Consumers should stay informed about the Federal Reserve’s decisions and adjust their financial strategies accordingly. With the potential for lower interest rates on mortgages, car loans, and credit cards, now may be an ideal time to consider refinancing or paying down existing debt.
What signals did Fed Chairman Jerome Powell convey regarding future monetary policy?
Fed Chairman Jerome Powell emphasized the Fed’s readiness to adjust monetary policy based on economic conditions. He noted that if the labor market shows signs of deterioration, the Fed is likely to implement more significant rate cuts, indicating a proactive approach to economic management.
| Point | Details |
|---|---|
| First Rate Cut in Four Years | The Federal Reserve cut the key interest rate by 0.5%, the first reduction in four years, indicating a shift in monetary policy. |
| Impact on Consumers | Beneficial for individuals with credit card debt, car loans, prospective home buyers, and stock investors. |
| Future Rate Cuts Anticipated | Chairman Jerome Powell anticipates two more cuts by year-end if economic conditions warrant. |
| Signal to Markets | Clear messaging to markets that the Fed is prepared to react to a weakening labor market with more rate cuts. |
| Uncertainty about Future Rates | While some rates may decrease, uncertainty remains about how quickly consumers will see relief in credit card and loan rates. |
Summary
The Federal Reserve rate cut marks a significant shift in U.S. monetary policy, benefitting consumers while also raising questions about the timing and extent of future reductions. As the Fed seeks to balance inflation control with economic growth, potential additional rate cuts suggest a proactive approach to maintain stability in both the labor market and consumer borrowing costs. Overall, the rate cut is viewed positively, paving the way for improved affordability and economic activity, though the degree of impact will depend on future economic data.