China tariffs have become a critical focal point in global trade relations, especially in light of the ongoing tensions stemming from the US-China trade war. These tariffs, designed to impact Chinese imports significantly, could yield unforeseen consequences not only for China’s economy but also for American consumers and businesses. Economists warn that imposing hefty tariffs can lead to higher prices and create supply chain disruptions, further straining economic ties between the two nations. As the implications of these tariffs ripple through the economy, they raise questions about their long-term effects on global trade dynamics and relationships with U.S. allies. Understanding the impact of tariffs on the economy is essential for grasping how these measures could reshape international commerce and diplomacy in the coming years.
Trade barriers imposed on China are reshaping the landscape of international commerce, influencing both economic policy and diplomatic relations. The introduction of tariffs has sparked discussions on their repercussions, highlighting concerns about increasing costs for consumers and potential disruptions in supply chains. As the United States looks to recalibrate its trade strategy, alternative economic interactions with countries like Mexico, Canada, and even within Europe have gained traction, complicating the existing global trade framework. The strategic implications of tariff policies warrant attention as various stakeholders navigate the complexities of shifting alliances and market dependencies. Ultimately, the economic implications of trade restrictions not only challenge existing paradigms but also set the stage for a new era of global negotiation.
The Potential Backlash of China Tariffs on the U.S. Economy
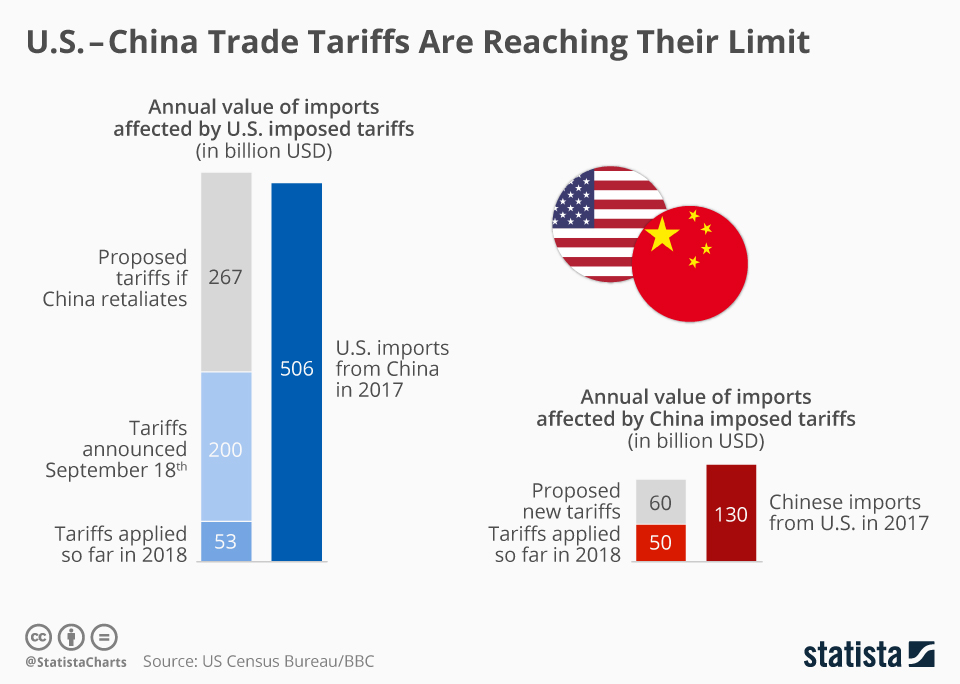
Imposing significant tariffs on imports from China can have far-reaching effects on the U.S. economy. While it may be intended to protect domestic industries, such a move is likely to lead to increased prices for American consumers as businesses pass on the higher costs of imported goods. Consumers might find essentials, such as electronics and clothing, significantly more expensive, leading to inflationary pressures that could stifle economic growth. Additionally, as these tariffs change the price dynamics, smaller businesses that rely on Chinese components could experience major disruptions, hampering their operational capacities and competitiveness.
Another concern is the ripple effect this could have on the broader supply chain. The U.S. economy is interconnected with global supply chains, and increased tariffs could lead to shortages of goods, as manufacturers struggle to source materials or components that may have been previously imported from China. This situation has the potential to exacerbate supply chain disruptions already felt from the pandemic, putting more strain on industries and potentially leading to layoffs. All in all, imposing tariffs may backfire, hurting the very economy it seeks to support.
Impact of the U.S.-China Trade War on Global Trade Relations
The U.S.-China trade war, characterized by the imposition of tariffs, has significantly altered global trade relations. Countries around the world are watching closely as the U.S. uses tariffs not only against China but also against other nations, including Canada and Mexico. This shift in policy could prompt affected countries to seek alternative trade agreements and alliances that may not include the U.S., potentially isolating America from key global players. As nations react to these tariffs, we could see a reshuffling of global trade partnerships that redefines existing trade routes and alliances, all while increasing geopolitical tensions.
Moreover, the move towards protectionism could encourage other countries to adopt similar stances, initiating a cycle of retaliation that would further fragment global trade networks. This domino effect could inhibit the free flow of goods and services, ultimately leading to a more complicated and expensive global market. Economists warn that this fragmentation could disrupt established supply chains, which depend on the smooth interchange of components and finished products across borders, underscoring the broader impact of enforcing tariffs.
Supply Chain Disruptions: Unforeseen Consequences of Tariff Policies
The imposition of tariffs can disrupt existing supply chains in multiple ways. For one, tariffs increase costs for raw materials and components that many manufacturers depend on, leading to increased production costs that may ripple throughout the supply chain. This ultimately affects pricing, delivery timing, and inventory management, making businesses less agile and responsive to market changes. Furthermore, reliance on Chinese components means that any trade barriers can cause significant delays or production stoppages, which can harm U.S. competitiveness in global markets.
As countries look for alternative suppliers to mitigate the impact of U.S. tariffs, they may find it challenging to identify partners that can match China’s capacity and efficiency. The geographical proximity of suppliers matters considerably; for example, shifting production to places like Vietnam may seem viable, but such regions may not yet have the established infrastructure or skilled labor force to handle higher production demands efficiently. This indicates that removing reliance on China for goods may not be as simple as shifting orders elsewhere, as adequate substitutes are not readily available, and potential short-term supply chain disruptions loom.
Tariff Implications for American Consumers and Businesses
The implications of implementing tariffs on imports from China extend beyond the boardroom and into the everyday lives of American consumers. Initially, consumers may not feel the impact immediately, but as companies adjust their pricing strategies to accommodate the increased costs of tariffs, higher prices are inevitable. Items that were once affordable can become luxury goods, disproportionately affecting lower-income households. This burden is compounded by the fact that many staple products include components sourced from China, which is vital for businesses seeking to maintain low production costs.
Moreover, American businesses face an uphill battle in navigating these tariffs while trying to remain competitive. Smaller enterprises, in particular, might lack the resources to absorb the added costs or pivot to alternative supply chains quickly. This financial strain can lead to reduced employment opportunities, as businesses may have to cut staff or halt expansion plans to maintain profitability amidst rising production costs. Ultimately, the end result is a cycle where tariffs meant to protect jobs can inadvertently lead to job losses and a more precarious economic situation for the average American.
Long-Term Economic Consequences of the U.S.-China Trade War
The long-term economic consequences of the U.S.-China trade war could be profound, shaping the future landscape of international trade and economic alliances. With the uncertain trajectory of tariffs galore, businesses may start relocating their operations to countries away from China to avoid the geopolitical risk associated with U.S. tariffs. However, this relocation requires significant investment, time, and resources, particularly when countries like Vietnam and India do not yet have the requisite infrastructure to fully absorb the manufacturing output displaced by tariffs.
Additionally, over the long-term, continued reliance on tariffs could stall innovation in various sectors. By insulating certain industries from foreign competition, tariffs disrupt the drive for businesses to innovate and improve their products. This can lead to stagnation within those industries, denying consumers the benefits of advancements and keeping prices high. The dynamic global economy thrives on competition, and imposing tariffs may hinder the U.S. from fully participating in this competitive landscape.
Geopolitical Risks Associated with Tariff Strategies
Tariff strategies can carry significant geopolitical risks that extend beyond economic impacts. By imposing tariffs on allies and trading partners alike, the U.S. risks alienating countries that have historically aligned with American interests. As China strengthens its diplomatic ties with these nations in response to U.S. tariffs, a more polarized global landscape could become a reality, with countries forced to choose sides. This potential realignment could lead to a diminished U.S. influence in international affairs as countries seek more balanced partnerships with other leading economies.
In light of geopolitical tensions, the U.S. might find itself in a precarious situation where its tariffs inadvertently empower China in its quest for global markets. Countries that previously relied on the U.S. for trade may look to China for alternatives that seem more stable, thus undermining U.S. credibility on the international stage. This not only damages economic interests but also complicates U.S. involvement in other global issues—ranging from security alliances to climate agreements—as countries perceived as marginalized might seek support from alternative powers.
China’s Strategic Responses to U.S. Tariff Policies
As the U.S. considers new tariffs, China has begun strategizing its response to mitigate the impact. One avenue may involve enhancing bilateral trade agreements with nations that may also feel the repercussions of U.S. tariffs. By aligning itself with European and Asian partners, China could fortify its economic standing and create a bloc that counters U.S. influence. This tactic underscores a move toward a more multipolar world, wherein various global players band together against unilateral American trade policies.
Moreover, China could also focus on self-reliance by bolstering domestic production capabilities and fostering home-grown industries. The goal here would be to reduce dependence on U.S. markets and mitigate the risks associated with international trade disruptions. By investing in technology and innovation, China can pivot away from being a manufacturing powerhouse reliant on exports, instead strengthening its position in high-value sectors. This long-term strategy not only buffers China against U.S. tariffs but also positions its economy for sustainable growth.
The Future of U.S.-China Trade Relations
The future of U.S.-China trade relations hangs in the balance as tariffs continue to create tensions between the two economies. Each new tariff announcement sends ripples through financial markets, further complicating prospects for future negotiations and trade agreements. With both sides entrenched in their positions, the path to resolution may involve lengthy negotiations and reciprocal concessions. This stalemate could deter investment in both countries, leaving critical sectors vulnerable and volatile.
As the economy ecosystems evolve, both nations must assess the broader implications of their trade policies and the potential for collaboration in the fields of technology, climate change, and security. A cooperative strategy could yield benefits that surpass the short-term gains from imposing tariffs. However, achieving such cooperation requires trust-building measures that currently seem elusive. The outlook remains uncertain, as the dual nature of competition and cooperation defines the trajectory of U.S.-China trade relations moving forward.
Examining Alternative Trade Partnerships to Offset Tariff Effects
In consideration of rising tariffs, countries are actively exploring alternative trade partnerships to mitigate their reliance on U.S. and Chinese markets. Building strong trade networks with countries in Africa, Southeast Asia, and Latin America can provide access to new markets and diversified supply chains. This diversification not only helps offset potential losses from tariffs but can also create avenues for economic growth in emerging markets.
Regions like the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) are likely to benefit as companies seek to relocate operations or source materials away from China. However, integrating alternative trade partnerships involves addressing logistical challenges, regulatory hurdles, and investing in up-to-date infrastructure. Countries keen on shifting their export strategies need to ensure they are prepared to navigate these complexities to avoid further economic disruptions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the potential impacts of China tariffs on the U.S. economy?
China tariffs could lead to increased prices for American consumers, supply chain disruptions, and potential labor shortages. These tariffs may exacerbate economic tensions and could weaken U.S. ties with its allies as countries seek to realign their trade relations.
How do China tariffs affect global trade relations?
The imposition of China tariffs can significantly alter global trade relations by prompting affected countries to seek new partnerships. If the U.S. increases tariffs, countries may pivot towards China for trade cooperation, which could foster stronger international ties between Beijing and its trading partners.
What role do tariffs play in the ongoing U.S.-China trade war?
In the U.S.-China trade war, tariffs serve as a tool to leverage negotiations and influence trade outcomes. The threat of high tariffs has led to uncertainty in both economies, impacting business strategies and trade flows, while potentially fostering an environment for countries to shift alliances.
What are the implications of China tariffs for supply chain disruptions?
China tariffs can create significant supply chain disruptions, as many companies rely on Chinese manufacturing for components. Increased tariffs may force businesses to seek alternative suppliers, which could lead to delays, increased costs, and a reevaluation of existing supply chains.
How might the imposition of high tariffs on China impact the prices of goods in the U.S.?
High tariffs on China are likely to result in increased costs for imported goods, which could lead to higher prices for consumers in the U.S. This inflationary pressure may affect various sectors, particularly in electronics, textiles, and consumer goods.
What challenges do U.S. consumers face with rising China tariffs?
U.S. consumers may face challenges such as higher retail prices as businesses pass on the costs of tariffs. Additionally, consumers could experience limited availability of products as companies adapt to changes in import costs and supply chain dynamics.
How could China tariffs influence future economic negotiations between the U.S. and China?
China tariffs could either escalate tensions or serve as a catalyst for renewed negotiations. If tariffs are viewed as a starting point for dialogue, they may prompt both countries to seek compromise to alleviate the economic strain and restore trade relations.
What are the consequences of China tariffs on U.S. imports?
The consequences of China tariffs on U.S. imports include potential reductions in import volumes, changes in manufacturing investments in other countries, and shifts in consumer purchasing patterns as people seek alternatives outside of China.
Could high tariffs on Chinese goods encourage domestic manufacturing in the U.S.?
Yes, high tariffs on Chinese goods may incentivize U.S. companies to invest in domestic manufacturing to avoid tariffs, potentially leading to job creation but may also require significant time and financial resources to ramp up production.
In what ways could China respond to U.S. tariffs?
China could respond to U.S. tariffs by imposing retaliatory tariffs on American goods, enhancing trade relations with other countries, and stimulating domestic consumption to mitigate the economic impact on its economy.
| Key Points | Details | |
|---|---|---|
| Impact of U.S. Tariffs on China | Potentially damaging to China’s economy. | |
| Economic Backfire on the U.S. | Could lead to higher consumer prices and supply chain disruptions. | |
| Global Relations | Tariffs may foster closer ties between China and U.S. allies. | |
| China’s Economic Strategies | China is preparing to adapt to potential tariffs by seeking new markets. | |
| Long-term Effects | Increased opportunity for China to strengthen international relations. | |
Summary
China tariffs could have significant implications for both the U.S. and global economy. While the aim might be to protect American industries, these tariffs could backfire by driving up costs for consumers in the U.S. and disrupting supply chains. Furthermore, they may inadvertently strengthen China’s diplomatic relationships with traditional U.S. allies, as these countries may seek closer ties in response to U.S. trade policies. As such, careful consideration and strategic planning are essential to avoid negative outcomes from tariff implementations.